Isolation transformers are used in drive (VFD / VSD) as well as many other applications to provide any of the following:
Voltage change: Isolation transformers can be used to supply a VFD that has a different input voltage from the system voltage. This could be useful especially when drives are purchased from overseas location that may have a different voltage rating.
Provide a stable line to ground voltage reference: Isolation transformers that have wye-grounded secondary can provide stable line to ground voltage to the drive. Some drives ‘require’ a grounded source to work properly and most drives in the market today will require some minor adjustment to the front-end noise filter circuit if applied in an ungrounded source supply.
Ground current control: By having a wye-grounded secondary isolation transformer, the ground currents originating at the VFD/motor (due to IGBT switching, stray capacitance etc.) have a well-defined path back to the source which is the secondary of the isolation transformer. (remember the isolation transformer is a separately derived source and hence ground current will have to return to the secondary neutral of the transformer)
Common mode noise control: Isolation transformer prevents transfer of common mode voltage from primary to secondary as well as from secondary to primary. This could help with issues related to data communication error due to presence of common mode voltage. Common mode noise is discussed again at the end of this article.
Provide required supply side impedance to the VFD for harmonic current control: Drives need a certain impedance on the supply side (input side) for harmonic control as well to prevent damage to drive from high short circuit currents. Isolation transformer provides the required impedance by virtue of its leakage reactance. Note here that the ‘effective’ impedance provided by the transformer will also depend on the rating of the transformer vs the rating of the drive. Use the calculator provided in this article to calculate the effective impedance of the isolation transformer at the rated drive load.
Mitigate voltage notching (for DC drives and drives with SCR front end) [See Voltage Notching for more information]. Isolation transformer provides the required supply side impedance required for controlling voltage notching.
Transient noise attenuation originating at the supply side. Isolation transformers are effective in attenuating transients originating on the supply side from affecting the drive.
Isolate drive from system voltage transient events: Isolation transformers provide protection from system generated voltage transients such as capacitor switching which in the absence of isolation transformer could cause an over voltage shutdown of VFD.
Harmonic Current Cancellation: For similar sized VFD, by using a combination of delta-wye and delta-delta transformers to feed two identical drives, the harmonic currents at the primary side of both transformers get some cancellation. This is due to the 30-degree phase angle shift when passing through delta-wye transformer. The current flowing through delta-delta will not experience any phase shift. If used wisely this design can lower the effective harmonic current at the service entrance location. Note that delta-delta transformer will not be able to provide a ground reference to the VFD.
Isolation transformers provide all the functions listed above and is often the preferred method to provide the required impedance for large drives. While line reactor provides many of the benefits of isolation transformer in a drive application, there are some key differences as well.
Drive Isolation Transformer Sizing
Drive isolation transformer can be selected by consulting with the drive manufacturer. If this is not possible, then the below chart can be used to as a guide to select the transformer kVA based on the drive rated horse power.
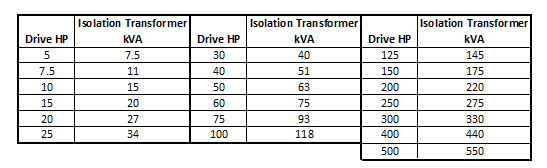
VFD isolation transformer sizing
Drive Isolation Transformer Impedance
Usually the impedance of the drive isolation transformer is between 4-6% and this value will vary between the drives and the application. A higher impedance may be required for any of the following cases:
Drive is applied close to the service entrance with high short circuit capability
The manufacturer of the drive asks for a higher minimum impedance
Additional harmonic control is desired
Often times a transformer is selected which could have a higher kVA than the rating of the drive. If the drive has a certain minimum required impedance then it becomes a question whether this ‘oversized’ isolation transformer is providing the required line impedance. Use the calculator below to find the effective impedance offered by the isolation transformer at the actual drive rating.
Isolation Transformer Effective Impedance Calculator
https://voltage-disturbance.com/variable-frequency-drive/why-use-an-isolation-transformer/



nice good post
ReplyDelete